Tolbachik lava field
 |
|
Tolbachik lava field |
|
|
|
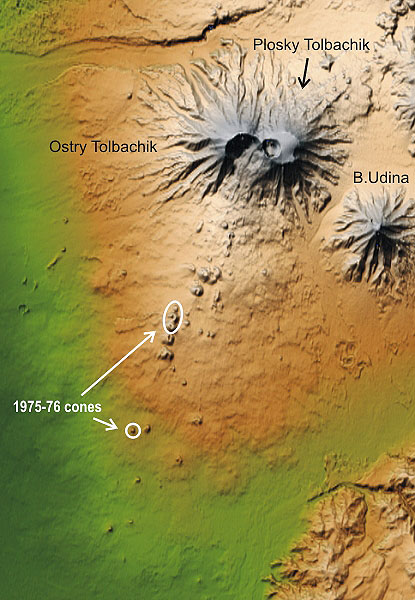
Tolbachik volcano is built by two coalesced late Pleistocene
cones: Ostry ("Sharp") Tolbachik and Plosky ("Flat") Tolbachik.
Ostry Tolbachik was partly destroyed by a sector collapse, likely in
the early Holocene time. Plosky Tolbachik is crowned with a summit caldera,
which hosts
a small shield volcano, now covered by a glacier. A smaller caldera and
a modern crater intermittently filled with a lava lake are located in
the western part
of the larger caldera. |